(001) 88451234 88455438

فناوران سپیدجامگان
طراح و تولیدکننده تجهیزات پیشرفته پزشکی با تمرکز بر نوآوری، بومیسازی و توسعه فناوریهای سلامت
Physiotherapy
What Is Physiotherapy?
The term Physiotherapy is derived from the combination of “Physio” (meaning physical) and “Therapy” (meaning treatment). Physiotherapy, or physical therapy, is a branch of paramedical science focused on treating muscular, skeletal, and neurological disorders using mechanical devices, non-invasive electrical currents, exercise therapy, and manual techniques. A physiotherapist evaluates joint and muscle function, manages weakness and pain caused by injuries or surgeries, and improves physical and motor performance—either independently or in collaboration with specialists in orthopedics, physical medicine, sports medicine, rehabilitation, and geriatrics.
Common Conditions Requiring Physiotherapy
- Injuries caused by trauma, accidents, fractures, sprains, dislocations, burns, sports injuries, and surgeries
- Loss of balance following stroke or cerebral palsy; peripheral and central nervous system disorders
- Skeletal deformities such as spinal curvature, flat feet, or bow legs
- Joint stiffness due to various causes
- Musculoskeletal complications from autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, Guillain-Barré, and arthritis
- Degenerative bone conditions such as osteoarthritis and sarcopenia
- Joint disorders, neurological tumors, or joint replacements
- Pelvic floor dysfunctions
- Physical and motor limitations in elderly individuals and occupational injuries
- Congenital deformities of joints, bones, or tendons
- Muscle spasms, tendon pain, and chronic muscular pain
- Functional limitations caused by limb amputation, diabetes, dialysis, or cardiac rehabilitation
- Even animal physiotherapy
In summary, physiotherapy focuses on pain management, inflammation reduction, and the restoration of movement and functional ability.
Types of Physiotherapy Devices
Physiotherapy devices are tools designed to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and improve physical performance in the mentioned conditions. These devices are non-invasive and safe, often working through controlled electrical or magnetic stimulation that penetrates tissue to enhance metabolism, improve healing, and restore natural body function. Since 1855, electrical generators have been used in physiotherapy, and later, electromagnetic fields were introduced to expand treatment applications.
What Is the Difference Between Electrical and Electromagnetic Therapy?
Electrical therapy, commonly known as Electrotherapy, uses controlled electrical currents to increase blood circulation, reduce inflammation, and relieve pain. The most popular form is TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation), which delivers mild electrical impulses through electrodes placed on the affected area. Sessions usually last between 20 and 60 minutes, depending on the device type, and are particularly effective in reducing localized pain and spasms.
Electromagnetic therapy, on the other hand, works through magnetic fields that have deeper tissue penetration and a wider range of therapeutic applications.
How Do Electromagnetic Waves Work in Physiotherapy?
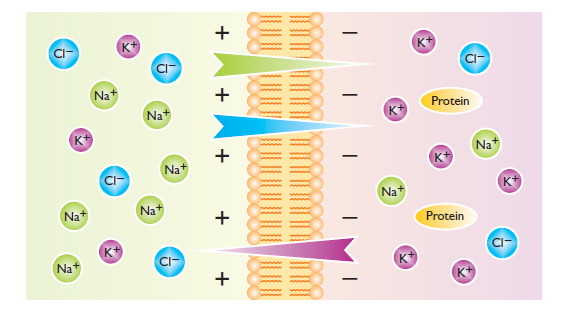
Electromagnetic fields play a significant role in nature and have been used in medical science for over two centuries. The Earth itself is a massive magnetic field. The human body, composed of billions of cells, maintains electric potential through cellular activity. When this electric energy decreases, body systems weaken. Studies show that electromagnetic fields can restore cellular potential, enhance oxygen consumption and blood flow, and facilitate ion exchange. This leads to improved metabolism, faster tissue repair, reduced inflammation, and enhanced nerve and muscle activity.
How Are Electromagnetic Waves Generated?
Electromagnetic waves can be produced in two main ways:
- Static Models: Devices that use permanent magnets, such as magnetic bracelets or accessories, maintain a constant magnetic field without external power.
- Dynamic Models: Devices like PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy) machines, which generate controlled magnetic pulses through an electric current passing in coils or applicators.
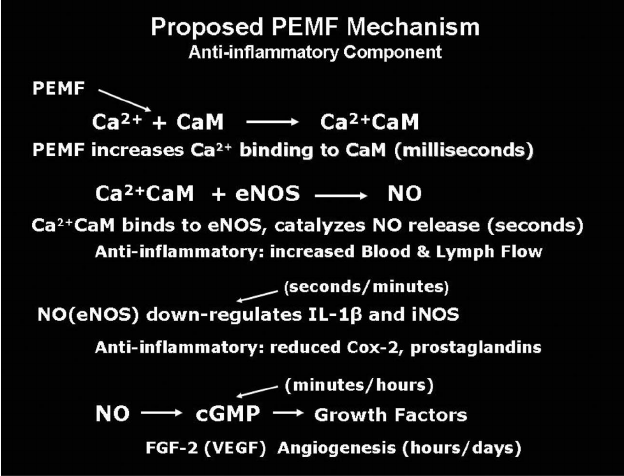
General Effects of PEMF Therapy on Health
- Pain relief and inflammation reduction
- Improved oxygenation and vasodilation
- Enhanced local blood circulation and angiogenesis
- Tissue regeneration and bone repair
- Improved muscle contraction and performance
- Localized fat reduction
- Enhanced cellular ion exchange and sodium-potassium pump activity
- Reduced vascular permeability and swelling
- Improved calcium transport and bone mineralization
- Increased ATP and nitric oxide production
- Enhanced collagen synthesis and growth factor release
- Reduced pro-inflammatory markers
- Increased release of endorphins and pain-modulating hormones
Medical Applications of PEMF Therapy
PEMF therapy is used in physiotherapy, rehabilitation, pain management, physical medicine, orthopedics, urology, gynecology, wound healing, neurology, weight management, and even veterinary medicine.
PEMF Indications in Physiotherapy and Pain Management
- Muscle spasms after sports injuries
- Chronic and acute musculoskeletal pain
- Muscle reactivation following atrophy or injury
- Bone healing and regeneration
- Pain relief in sciatica, lumbago, meniscus injuries, and pelvic disorders
- Management of urinary or fecal incontinence caused by various factors
- Treatment of joint, ligament, and tendon injuries
- Supportive therapy for bursitis, capsulitis, fibromyalgia, and carpal tunnel syndrome
- Prevention and treatment of osteoporosis
- Reduction of local pain, swelling, and inflammation
- Neuromuscular stimulation in patients with motor disorders
- Combination therapy after orthopedic surgeries
- Supportive therapy in overweight patients with movement limitations
- Accelerated wound healing in bedridden or post-surgery patients
- Reduced recovery time after immobilizing illnesses
- Strengthening of pelvic and core muscles
- Improvement in numbness and tingling due to conditions like spondylosis
- Muscle relaxation and improved sleep quality
Contraindications of PEMF Therapy
- Patients with acute infections, heart disease, vascular blockages, hypertension, or cancer
- Women during menstruation, pregnancy, or breastfeeding
- Patients with pacemakers or metal implants
- Open wounds or bleeding lesions
- Patients undergoing chemotherapy or using corticosteroids
Are There Any Side Effects of PEMF Therapy?
When used according to the patient’s condition, pain level, and proper device settings, PEMF therapy has no side effects. It is a non-invasive, safe, and cost-effective method with proven clinical benefits.
Duration and Frequency of PEMF Therapy Sessions
The number and duration of PEMF sessions depend on the patient’s diagnosis, treatment goals, and device type. Generally, each session lasts between 5 to 15 minutes and may be performed 3–4 times per week, as prescribed by a physiotherapist.
Combination Therapy with PEMF
PEMF therapy can be effectively combined with other physiotherapy modalities such as manual massage, stretching exercises, low-level laser therapy, TENS, or ultrasound. However, even as a standalone treatment, PEMF is highly effective for restoring tissue function.
Cost of PEMF Physiotherapy
The cost of PEMF sessions depends on the type of device, clinical services provided, and additional therapies included in the treatment plan.
Who Performs PEMF Therapy?
PEMF therapy should always be performed by a qualified physician or physiotherapist with a proper understanding of anatomy and rehabilitation techniques to avoid potential harm.
Conclusion
PEMF technology offers a modern, non-invasive approach to reduce pain and inflammation, restore movement, and enhance recovery after injuries, surgeries, or chronic conditions. It can be used independently or in combination with other physiotherapy methods for optimal results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is a prescription required for PEMF therapy?
Yes. A physiotherapist or physician must assess the patient’s condition and determine the appropriate session duration, frequency, and intensity based on individual needs.
2. How effective is PEMF therapy?
Clinical studies show that PEMF therapy significantly improves pain reduction, inflammation control, and functional performance, both as a standalone and in combination with other physiotherapy techniques.
3. Where is PEMF therapy available?
PEMF devices are available in physiotherapy centers, rehabilitation clinics, and medical facilities offering physical medicine and recovery treatments.